Retained Earnings in Accounting and What They Can Tell You

For example, a high credit balance in accounts payable might signal potential liquidity issues, while substantial retained earnings suggest profitability and growth potential. Financial ratios, such as the current ratio or debt-to-equity ratio, rely on the accurate representation of these balances for meaningful analysis. There is no change in the shareholder’s when stock dividends are paid out, however, you’ll need to transfer the amount from the retained earnings part of the balance sheet to the paid-in capital. The amount transferred to Accounting for Churches the paid-in capital will depend upon whether the company has issued a small or a large stock dividend. Since cash dividends result in an outflow of cash, the cash account on the asset side of the balance sheet will get reduced by $100,000. This outflow of cash would also lead to a reduction in the retained earnings of the company as dividends are paid out of retained earnings.
Key Takeaways
- Retained earnings and profits are related concepts, but they’re not exactly the same.
- The amount of a corporation’s retained earnings is reported as a separate line within the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet.
- In accounting and bookkeeping, a credit balance is the ending amount found on the right side of a general ledger account or subsidiary ledger account.
- The retained earnings portion of stockholders’ equity typically results from accumulated earnings, reduced by net losses and dividends.
- Retained earnings refer to the historical profits earned by a company, minus any dividends it paid in the past.
- To make informed decisions, you need to understand how financial statements like the balance sheet and the income statement impact retained earnings.
- Changes in unappropriated retained earnings usually consist of the addition of net income (or deduction of net loss) and the deduction of dividends and appropriations.
Conversely, when a company incurs a net loss or declares dividends, it will debit the retained earnings account, thereby decreasing its balance. Retained earnings are a type of equity and are therefore reported in the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet. Although retained earnings are not themselves an asset, they can be used to purchase assets such as inventory, equipment, or other investments. Therefore, a company with a large retained earnings balance may be well-positioned to purchase new assets in the future or offer increased dividend payments to its shareholders. Due to the nature of double-entry accrual accounting, retained earnings do not represent surplus cash available to a company.
Related AccountingTools Courses
This means that retained earnings typically increase with credits and decrease with debits. A positive credit balance indicates accumulated profits, while a negative balance may suggest accumulated losses or deficits. Net income increases Retained Earnings, while net losses and dividends decrease Retained Earnings in any given year.
- This article provides a comprehensive overview of what you need to know about retained earnings, but feel free to jump straight to your topic of focus below.
- Your company’s equity investors, who are long term investors, will seek periodic payments in the form of dividends as a return on the money invested by them in your company.
- It typically includes the beginning retained earnings, net income, dividends paid, and ending retained earnings.
- Businesses take on expenses to generate more revenue, and net income is the difference between revenue (inflow) and expenses (outflow).
- If they are confident that this surplus income can be reinvested in the business, then it can create more value for the stockholders by generating higher returns.
- As a result, each shareholder has additional shares after the stock dividends are declared, but their stake remains the same.
- Where cash dividends are paid out in cash on a per-share basis, stock dividends are dividends given in the form of additional shares as fractions per existing shares.
Understanding Credit Balances for Accurate Financial Reporting

The retained earnings are calculated by adding net income to (or subtracting net losses from) the previous term’s retained earnings and then subtracting any net dividend(s) paid retained earnings normal balance to the shareholders. The income statement (or profit and loss) is the first financial statement that most business owners review when they need to calculate retained earnings. This document calculates net income, which you’ll need to calculate your retained earnings balance later.
How to account for retained earnings
If a business sold all of its assets and used the cash to pay all liabilities, the leftover cash would equal the equity balance. When one company buys another, the purchaser buys the equity section of the balance sheet. The income statement calculates net income, which is the balance you have after subtracting additional expenses from the gross profit. If the company had a total of 100,000 outstanding shares prior to the stock dividend, it now has 110,000 (100,000 + 0.10×100,000) outstanding shares. So, if you as an investor had an 0.2% (200/100,000) stake in the company prior to the stock dividend, you still own a 0.2% stake (220/110,000), meaning nothing changes as far as the company is concerned.

Account
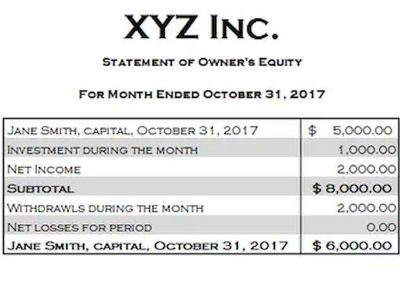
These programs are designed to ledger account assist small businesses with creating financial statements, including retained earnings. To simplify your retained earnings calculation, opt for user-friendly accounting software with comprehensive reporting capabilities. There are plenty of options out there, including QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks. A statement of retained earnings details the changes in a company’s retained earnings balance over a specific period, usually a year.

